Understanding these mechanisms can shed light on the factors contributing to facial aging and potentially guide the development of targeted interventions.
Skull and Facial Bone Changes with Age:
As individuals age, several structural changes occur in the skull and facial bones, resulting from a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. These changes include:
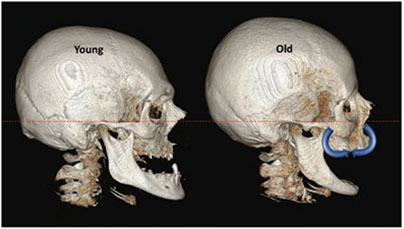
Bone Loss: The natural aging process leads to a decrease in bone density and volume, known as osteoporosis. This affects the facial bones, particularly the maxilla and mandible, causing them to shrink and lose their original shape and contour.
Resorption: The process of bone resorption becomes more prevalent with age. Osteoclasts, specialized cells responsible for breaking down old bone tissue, become more active, resulting in a net loss of bone mass. This resorption affects the bones of the eye sockets (orbits), cheeks (zygomatic bones), and jawline (mandible), leading to a reduction in facial projection and volume.
Facial Asymmetry: Over time, the balance between bone resorption and formation may be disrupted, leading to facial asymmetry. This can be attributed to differential bone loss in various facial regions, including the orbits, zygomatic arches, and mandible.
Effects on Skin and Appearance:
The changes in the skull and facial bones associated with aging have significant repercussions on the skin and overall appearance of the face. These effects include:
Wrinkles and Sagging: As the facial bones diminish in volume, the overlying skin loses support, leading to the development of wrinkles and fine lines. The reduced bone structure also contributes to sagging skin, particularly in the cheeks, jawline, and around the eyes.
Loss of Facial Contours: The reshaping and resorption of the facial bones contribute to the loss of distinct facial contours, such as a well-defined jawline and prominent cheekbones. This results in a flatter, less defined appearance.
Changes in Eye Area: The thinning of the orbital bones can cause a hollowing effect around the eyes, leading to the formation of under-eye bags and a sunken appearance. Additionally, the loss of bone volume in the upper jaw can contribute to drooping of the upper eyelids.
Altered Proportions: The changes in facial bone structure can affect the proportions of the face, such as the ratio of the lower face to the upper face. These alterations can result in an aged, imbalanced appearance.
Preventive Measures and Interventions:
While aging-related changes in the skull and facial bones are inevitable, certain preventive measures and interventions can help mitigate their impact on the skin and facial appearance:
Lifestyle Factors: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sun protection can promote overall skin health and minimize the effects of aging.
Dermal Fillers: Injectable dermal fillers containing substances like hyaluronic acid can be used to restore lost volume and enhance facial contours, temporarily reversing some of the age-related changes.
Surgical Interventions: Procedures such as facelifts, brow lifts, and eyelid surgeries can address more significant facial sagging and restore a more youthful appearance by repositioning tissues and tightening the skin.
Conclusion:
The aging process impacts not only the skin but also the underlying skull and facial bones, leading to noticeable changes in facial appearance. The gradual loss of bone density, bone resorption, and facial asymmetry contribute to wrinkles, sagging skin, loss of facial contours, and altered proportions.
These changes can result in a less youthful and less defined appearance. While complete prevention of these changes is not possible, adopting a healthy lifestyle and considering interventions like dermal fillers or surgical procedures can help minimize the effects of aging on the face.
Further research in this field may provide insights into innovative approaches to rejuvenate the facial structures and enhance overall facial aesthetics, improving the quality of life for individuals as they age.
